Softer than expected economic growth in China (see discussion) has finally spurred the PBoC into action. However, rather than undertaking asset purchases that would inject reserves into the overall banking system, the PBoC forced liquidity directly into state-owned banks.
NY Times: – With industrial production growing at the slowest pace since the worst of the global financial crisis and foreign direct investment in a tailspin, China appears to have taken the unusual step of using monetary stimulus in an attempt to forestall further economic weakness.Â
China’s central bank has lent 100 billion renminbi, or $16.2 billion, to each of the country’s five main, state-controlled banks, bankers and economists said Wednesday, although the central bank and the five banks involved stayed silent. The seemingly stealthy decision to inject a total of $81 billion into the banking system this week came as the Chinese economy, like many economies in Europe, has slowed over the summer, although still expanding at a pace that would be the envy of most countries around the world.
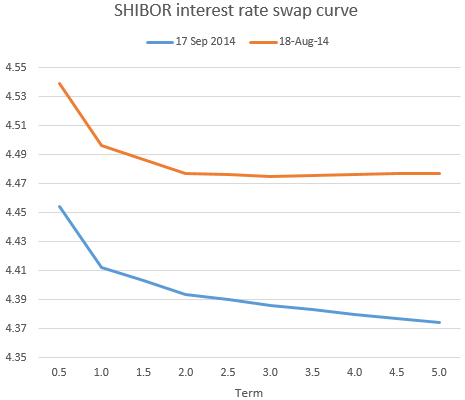
This is probably the least effective QE-style action, as state-owned lenders are unlikely to efficiently deliver capital into the private sector. But the fact that the PBoC has taken this action tells us this could be the start of a longer monetary stimulus effort. The markets are not expecting a near-term economic improvement and instead pricing in a prolonged battle to accelerate growth. China’s SHIBOR rate swap curve has become more inverted than a month ago with expectations of further rate declines.
Â

Some form of stimulus was already being priced in, which is in part what generated the recent stock market rally.

Source: Investing.com
Now the PBoC joins other major central banks in expanding “unconventional” monetary policy efforts. The impact of such actions on economic growth however remains highly uncertain, particularly in the face of softening property markets and weaker corporate balance sheets.