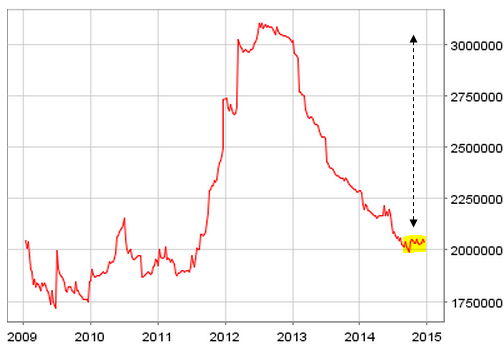
If Mario Draghi was lacking ammunition to initiate an outright quantitative easing program in the Eurozone, he certainly has it now. Even the staunchest opponents will have a tough time arguing against the need for a more aggressive approach to monetary easing. Here are five reasons:
1. The take-up on ECB’s TLTRO offering (see post) fell far short of the ECB’s goals. Indeed the demand in the second round of the offering came in at €130 bn, putting the total take-up at €212bn – well below the €400 billion allowance. Since the TLTRO financing is linked to bank lending, the program to some extent relies on demand for credit from businesses and consumers. And that demand has been lackluster in the past couple of years. Therefore the initiatives announced by the ECB last summer, including ABS and covered bond purchases, are simply insufficient for the type of monetary expansion (of about €1 trillion) the central bank would like to see in the Eurozone.
|
|
| Eurosystem consolidated balance sheet (source: ECB) |
2. Some Economic data out of the Eurozone shows recovery stalling. Italian industrial production and French labor markets are just two examples.
|
|
| Source: Investing.com |
|
|
| Source: Investing.com |
3. With the collapse of oil prices, the Eurozone is bracing for deflation. German 5-year breakeven inflation expectations are now at zero. And Europe’s central bankers are fearful of repeating Japan’s decade-long struggle with deflation.
|
|
| Source:Â @PlanMaestro |
4. While the euro has declined significantly against the dollar, it remains quite strong on a trade-weighted basis. This is putting downward pressure on prices (via cheaper imports) and is disadvantaging some of the Eurozone-based exporters. A more aggressive easing effort would force the euro lower.